Murina cyclotis
Round-eared Tube-nosed Bat
Morphological description Life history Distribution Habitat Roost sites and roosting patterns Emergence and flight pattern Foraging behaviour Echolocation calls Status and protection
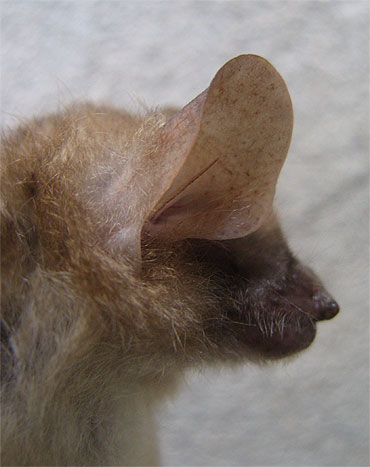
Morphological Description
· Dorsal fur is yellow brown or orange brown with grey hair roots. Ventral fur is pale with brownish tinge and looks darker than M. leucogaster . In a colour variant, the dorsal fur is grayer without an orange tinge, and the ventral fur is pale without a brownish tinge.
· The ears are rounded without an emargination on their posterior borders.
· The feet, wing membrane, tail membrane are hairy.
· Total length 80-90 mm (including body and tail length). Average forearm length 32.0 mm (range 29.7-34.5 mm, as given by Bates & Harrison 1997). Average wingspan is 230 cm.
· Average weight 8.5-12.5 g.
Life history
· Mating season is little known. Pregnant females in Malaysia were recorded to carry two foetuses from February to May (Medway 1983).
Distribution
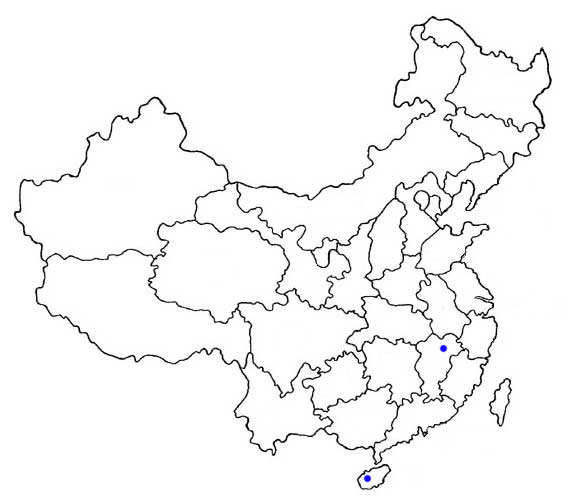
The mainland Chinese distribution is shown by dots on the map (as given by Zhang et al. (1997) and Wang (2003)). But we presume that the dot in Jiangxi Province might be not correct for this species. In southern Yunnan Province, the distribution needs to be investigated in further surveys.
Habitat
· Woodland is typical habitat.
· Lowland forests are important for them, especially tropical rainforests. The altitude of habitat generally is less than 1500 m (Bates & Harrison 1997).
· This species also inhabits coastal areas (humid regions) (Medway 1983).
Roost sites and roosting behaviour
· Roost is in caves.
· Their diurnal roosts also include large dead and dry leaves of the cardamom plant (Bates & Harrison 1997).
· This species often shares roosts with other bat species. Jinshuo Zhang trapped the bats by mist net at the entrance of caves in Vietnam , and found this species sharing cave roosts with more than 10 bat species.
Emergence and flight pattern
· Emerges in the early evening.
· Flight is relatively slow but maneuverable.
Foraging behaviour
· Forages at open areas of forests.
· The diet mainly consists of insects, especially moth.
Echolocation calls
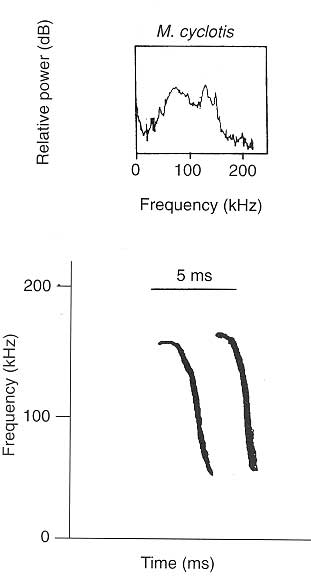
· The echolocation call is frequency modulated, brief and covers a wide range of frequencies. Average values for round-eared tube-nosed bat echolocation calls in Malaysia, as given by flight cage recordings made by Kingston et al. (1999) are listed below:
Start frequency: 143-180 kHz
End frequency: 38-73 kHz
Frequency of most energy: 54-137 kHz
Call duration: 1.2-4.1 ms
Status and protection
· There is no estimation of population size for China.
· Round-eared tube-nosed bats are at LR/lc, assessed by the Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2006) and are not listed in the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Wildlife in 1989.
· Caves and forests should be protected as their habitats.