Murina leucogaster
Greater Tube-nosed Bat
Baifu Guanbifu
Morphological description Life history Distribution Habitat Roost sites and roosting patterns Emergence and flight pattern Foraging behaviour Echolocation calls Status and protection
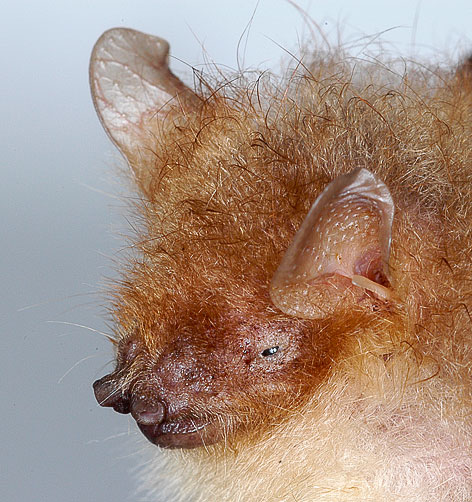


Morphological Description
· Dorsal fur is reddish-brown to brownish-grey, with isolated white hairs. Ventral fur is pale. Tail hairy. As with all Murina, nostrils form short tubes.
· The ears are relatively narrow and short.
· Forearm length 37.9 mm, 41.1 mm (adult males); (range 40-43 mm, as given by Smith & Xie 2008).
Life history
· Little known.
Distribution
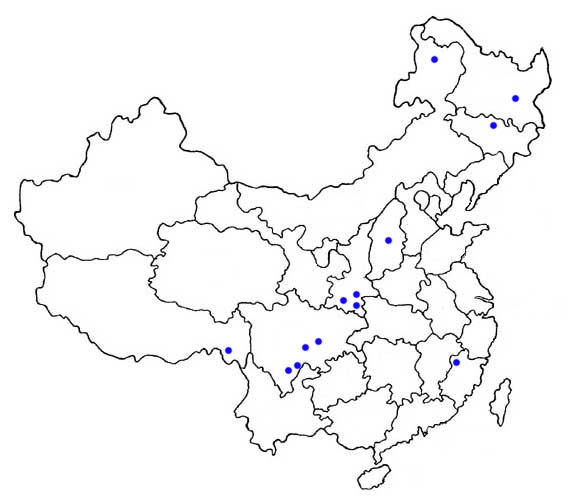
The mainland Chinese distribution is shown by dots on the map (as given by Zhang et al. (1997) and Wang (2003)). Widely distributed in E China and extends across Asia.
Habitat
· Forage in forests and open areas (Smith & Xie 2008).
Roost sites and roosting behaviour
· Roost is in caves. Also roosts in trees and houses (Smith & Xie 2008).
· Forms very large clusters during hibernation.
Emergence and flight pattern
· Not known.
Foraging behaviour
· Forages at open areas and in forests.
· Presumably insectivorous.
Echolocation calls
· Not known.
Status and protection
· There is no estimation of population size for China.
· Greater tube-nosed bats are at LR/lc, assessed by the Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2006) and are not listed in the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Wildlife in 1989. In China they are listed as RL-LC (Smith & Xie 2008).
· Caves and forests should be protected as their habitats.
