Pipistrellus abramus
Japanese pipistrelle
Morphological description Life history Distribution Habitat Roost sites and roosting patterns Emergence and flight pattern Foraging behaviour Echolocation calls Status and protection
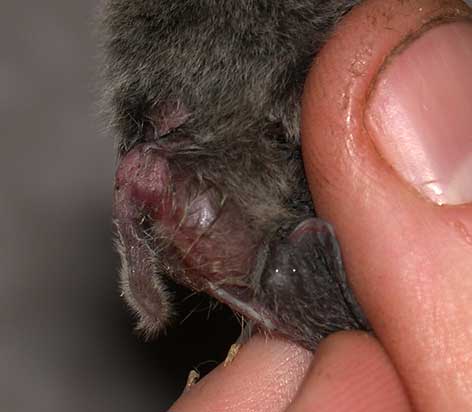
Morphological Description
· Dorsal fur is grey-brown. Ventral fur is grey.
· This is a small bat. Forearm length 29.4 - 33.7 mm. Body mass 3.9 - 6.5g.
· Male has a very long penis (up to 15 mm - top right).
· Belongs in the P. javanicus subgroup (Corbet & Hill1992). Tragus about a third the height of the ear, rounded at tip.
Life history
· Little known.
Distribution
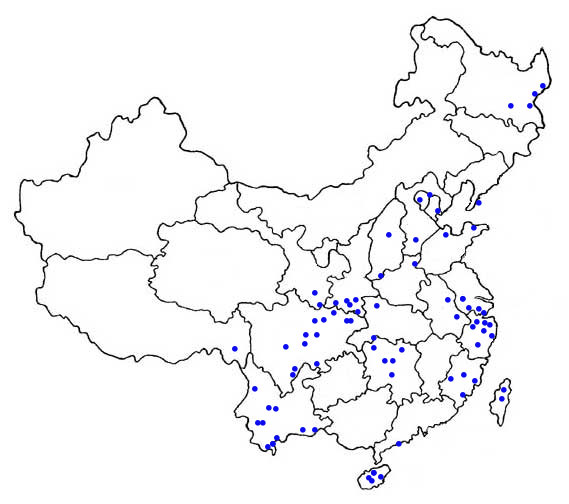
Found in China and Japan. The Chinese distribution is shown by dots on the map (as given by Zhang et al. (1997).
Habitat
· A common bat in towns and villages. Even seen in the centre of cities such as Beijing.
Roost sites and roosting behaviour
· Roosts in buildings, often under tiles. Roosts may be large.
Emergence and flight pattern
· An edge species which flies often along tree lines.
Foraging behaviour
· Little known.
Echolocation calls
The echolocation calls show clear frequency modulation, with the call beginning at high frequency and ending at a lower frequency, and ending with a more narrowband tail at times.
Analysis of power spectra shows that the maximum power of the call is at a frequency of approximately 43.8 - 52 kHz (average 48 kHz). A spectrogram, waveform and power spectrum of a typical call are shown below. To listen to 10x-expanded calls, click here (387 kB).
Status and protection
· There is no estimation of population size in China for this species.
· Japanese pipistrelles are not, assessed by the Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2006) and are not listed in the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Wildlife in 1989. They are widespread on a global scale and very common in places.
· Houses and buildings should be protected as their habitats.