Scotophilus heathii
Greater Asiatic Yellow House Bat
Morphological description Life history Distribution Habitat Roost sites and roosting patterns Emergence and flight pattern Foraging behaviour Echolocation calls Status and protection


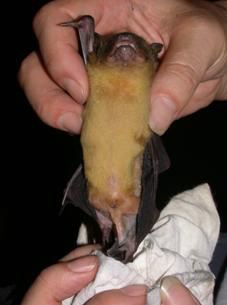
Morphological Description
· Dorsal fur is yellow-brown and looks a little bit green. Ventral fur is lighter than dorsal fur.
· Juveniles are lighter than adults.
· This bat is relatively large in Microchiroptera in China. Average forearm length is 58 mm.
Life history
· This bat is sometimes used in studies of mammalian reproduction. It is monoestrus. Pakrasi & Tiwari (2007) reported the preimplantation embryonic development in this species.
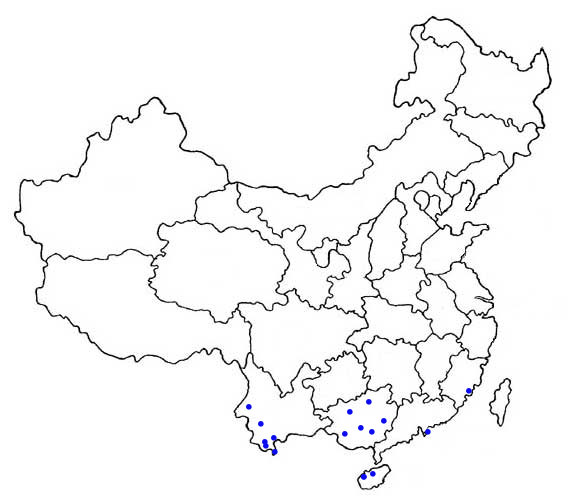
Distribution
The mainland Chinese distribution is shown by dots on the map (as given by Zhang et al. (1997) and Wang (2003)).
Habitat
· Can be found in towns and villages. In Xishuangbanna, southern Yunnan Province, the tropical rainforests are important habitat for this species.
Roost sites and roosting behaviour
· Roosts in buildings, caves and trees.
Emergence and flight pattern
· We used mist nets for trapping this bat in Xishuangbanna tropical rainforests and found that they forage in open spaces in rainforests.
Foraging behaviour
· The diet mainly consists of insects, but has taken fruit in captivity.
Echolocation calls
· Not known.
Status and protection
· There is no estimation of population size in China for this species.
· Greater Asiatic yellow house bats are at LR/lc, assessed by the Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN, 2007) and are not ed list in the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Wildlife in 1989.
· Caves, buildings, trees and rainforests should be protected as their habitats.