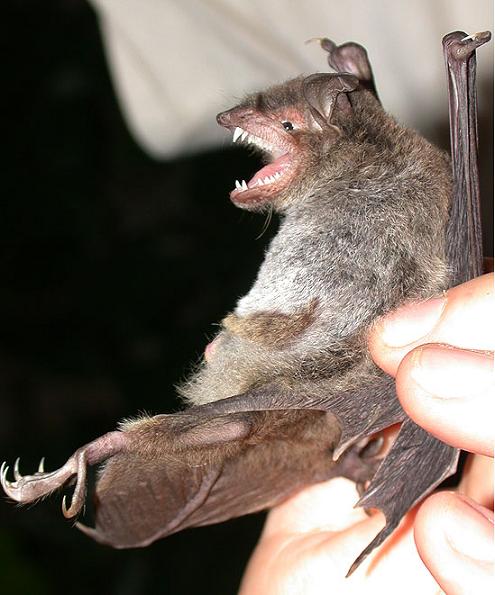
Rickett's big-footed bat, Fishing bat
Myotis ricketti
Morphological description Life history Distribution Habitat Roost sites and roosting patterns Emergence and flight pattern Foraging behaviour Echolocation calls Status and protection
Although Simmons (2005) uses M. ricketti, Smith & Xie (2008) believe that M. pilosus is and older synonym and hence the proper name for this species.
Morphological Description
· Dorsal fur is black-grey. Ventral fur is grey or white-grey.
· Juveniles are lighter than adults.
· Average forearm length 55.0-61.0mm. Average wingspan is 34.8cm.
· Longer feet than any other myotis species in China, 17.0-22.0mm (Ma et al. 2003).
· Average body mass (as given by Ma et al. 2003) 20.0-30.0g.
Life history
Mates in autumn, including during the hibernation period.
· Single young or occasionally twins born in spring.
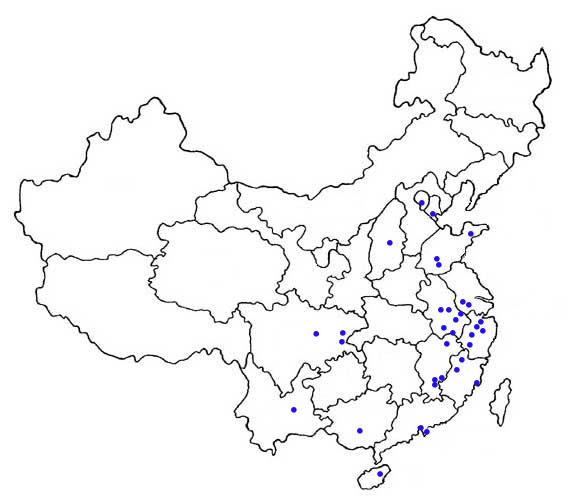
Distribution
The distribution in China is shown by the dots on the map (as given by Zhang et al. 1997; Ma et al. 2003).
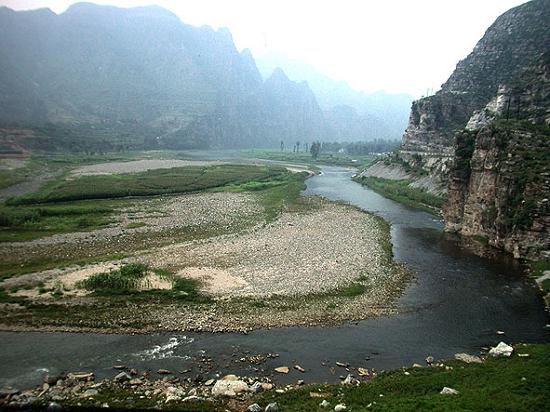
Habitat
Large areas of water, such as lakes, reservoir, and large still rivers provide important habitats for feeding.

Roost sites and roosting behaviour
Summer roost: nursery roosts are found from May and June and can be in buildings such as the Dule temple, Tianjin .
· Winter roost: hibernates in caves. Both summer roosts and winter roosts can be found in the same cave e.g. at Sihe , Fangshan district, Beijing .
· This species often share their roosts with other bat species, even with swifts (e.g. Temple Dule , Ji county, Tianjin ).
Emergence and flight pattern
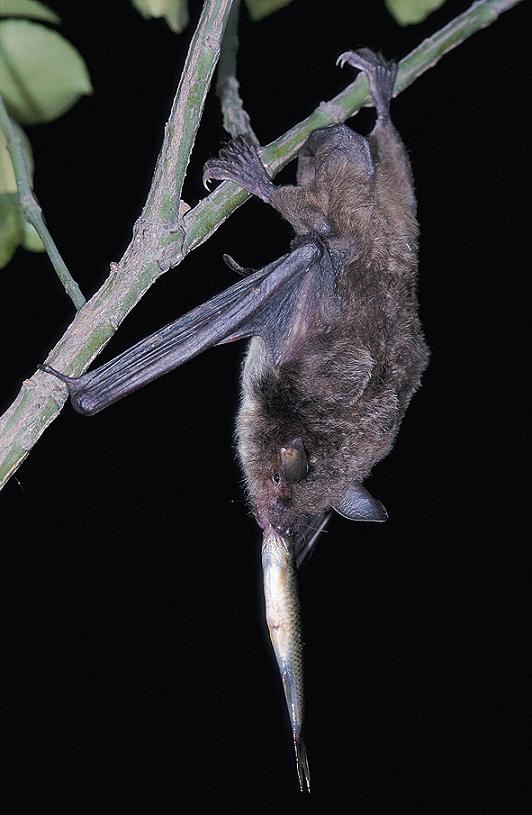
Flight is rapid and agile. Flies fast above the surface of the water to catch fish.
Foraging behaviour
Forages in low-medium woodland and over water. The diet mainly consists of 3 species of small fish, Zacco platypus , Carassius auratus , Phoxinus lagowskii and 7 orders of insects, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Homoptera, Ephemeroptera, Hemiptera, Diptera, and Hymenoptera. The percentage volume of fish in diet is more than 60%. (Ma et al. 2003, 2006).


Echolocation calls
The echolocation call is frequency modulated.
To listen to the call of the fishing bat click here
Size of sound file: 12 kb
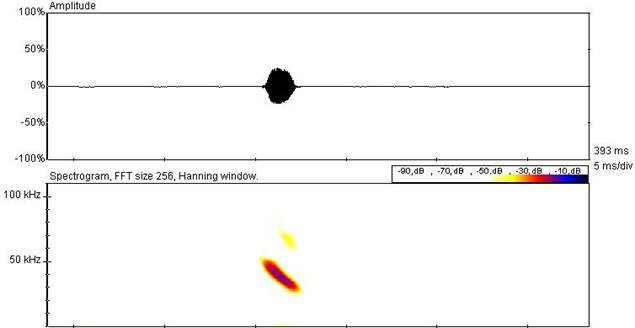
Average values for a fishing bat echolocation call, as given by Ma et al. 2003, are listed below:
Interpulse interval: 108.8ms; Call duration: 4.08ms; Minimum frequency: 27.68 kHz; Maximum frequency: 70.84kHz The spectrogram below shows clear frequency modulation, with the call beginning at high frequency and ending at a lower frequency. The maximum power of the call is at a frequency of approximately 41.6kHz (Ma et al. 2003).
Status and protection
There is no estimation of population size for China.
· Fishing bats are listed as at LR/nt (Lower Risk/ not threatened) worldwide (Hutson et al. 2001). They are not listed in the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Wildlife in 1989. Caves and old buildings should be protected as important roost sites.
